When it comes to fertility, factors such as hormonal and metabolic health matter. And in order to increase your chances for conception, nutrition can help. Read below to learn more about what infertility means, what nutrients can support fertility, and what foods and supplements you can consume today to increase your chances of becoming pregnant.
What does it mean to be infertile?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infertility is defined as being unable to become pregnant after 12 months of regular, unprotected sex (1). The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reports that about 12-percent of women between the ages of 15 and 44 years are infertile (2). However, you should know that men can also be infertile. Research shows that about 20 to 30-percent of males solely contribute to infertility cases (3).
In men, infertility may be a result of factors such as injury or trauma to the testicles, certain medicines or supplements, cancer treatments like chemo or radiation, as well as certain health issues like diabetes (2). Not to mention that men are more likely to be infertile if they engage in heavy alcohol use, smoking, steroid use, or illicit drug use. Hormonal issues or certain genetic issues can also cause infertility in men.
In women, dysfunction in organs like the ovaries, uterus, or fallopian tubes, or in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus in the brain, and age can lead to becoming infertile (2). Other factors that can increase risk of becoming infertile in women include:
- Excess alcohol use (more than one standard drink per day)
- Smoking
- Extreme weight gain or loss
- Excess physical or emotional stress that can impact the menstrual cycle
What nutrients can support fertility?
Experts also suggest that what you eat may play a role in fertility. Researchers at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health suggest that the nutrients below may support fertility (4):
- Folic acid
- Vitamin B12
- Omega-3 fatty acids
What foods and supplements can a person take to support fertility?
Researchers suggest that a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, may support fertility. This diet includes daily intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats as well as weekly intake of protein-rich foods like fish, poultry, beans, and eggs (5). This eating plan also suggests moderate portions of dairy products and limited intake of red meat.
Experts also suggest that to support fertility you should (6):
- Avoid trans fats and instead choose unsaturated fats to reduce inflammation in the body. Nuts, seeds, plant-based oils, and cold-water fish like sardines and salmon contain unsaturated fats.
- Increase fiber intake through eating complex carbohydrates like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to help control blood glucose levels.
- Focus on fluids like water and whole milk versus sugary drinks and limit intake of caffeine in drinks like tea, coffee, or diet cola.
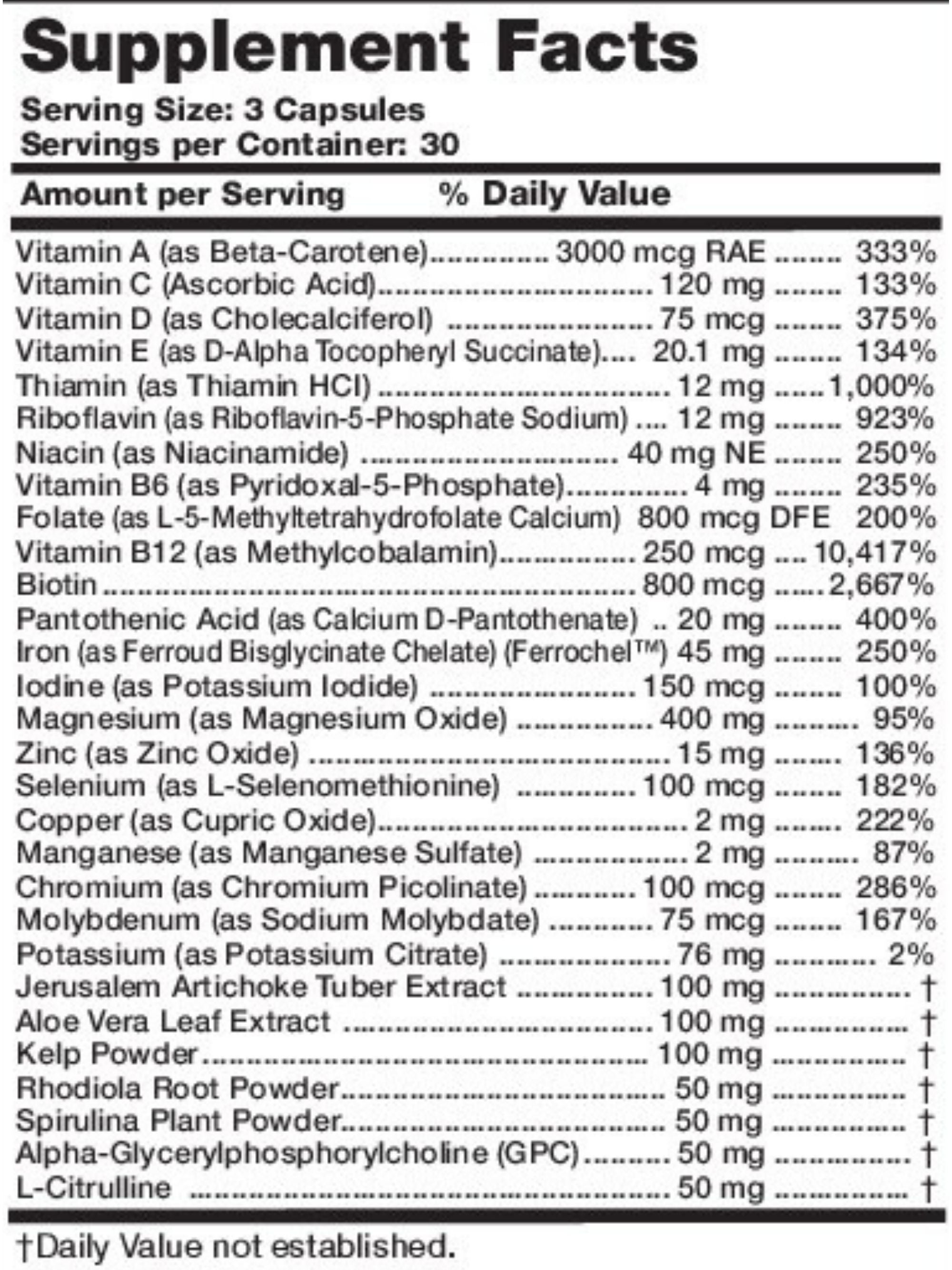
- Take certain supplements like folic acid, iron, or a prenatal multivitamin. You can also obtain iron from foods like whole-grain cereals, spinach, beans, pumpkin, tomatoes, and beets
Also, consume plenty of antioxidants daily to protect the egg and sperm from cell damage caused by oxidative stress (7,8). You can consume these in the form of capsules or in foods like produce and whole grains.
Bottom line on fertility and nutrition
Although changes in what you eat may not solve all fertility issues, it can help in most adults. Therefore, if you’re looking to conceive, a balanced diet of protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats may help improve your chances.
References:
- World Health Organization (accessed on January 27, 2021) “Infertility definitions and terminology.” https://www.who.int/teams/sexual-and-reproductive-health-and-research/areas-of-work/fertility-care/infertility-definitions-and-terminology
- Centers for Disease Control (last reviewed January 16, 2019) “Infertility FAQs.” https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/index.htm
- Vander Borght, M. and Wyns, C. (December 2018) “Fertility and infertility: Definition and epidemiology.” Clin Biochem., 62:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.03.012.
- Shmerling, MD, R.H. and A. Shmerling, MD, MPH (May 31, 2018) “Fertility and Diet: Is there a connection?” https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/fertility-and-diet-is-there-a-connection-2018053113949
- Mayo Clinic (June 21, 2019) “Mediterranean diet: A heart-healthy eating plan.” https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/mediterranean-diet/art-20047801
- Harvard Health Publishing Harvard Medical School (published May 2009) “Follow The Fertility Diet?” https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/follow-fertility-diet
- Silvestris, E., Lovero, D., & Palmirotta, R. (2019). “Nutrition and Female Fertility: An Interdependent Correlation.” Frontiers in endocrinology, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00346
- UPMC Health Beat (May 29, 2019) “Fueling Fertility: How Nutrition Can Improve Your Chances.” https://share.upmc.com/2019/05/fueling-fertility-how-nutrition-can-improve-your-chances/









Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.