Vitamin D is a vital nutrient that you need for optimal bone health, immune health, and for reducing inflammation in the body (1). Statistics show that about 24-percent of people in the United States, 37-percent in Canada, and 40-percent in European countries are deficient in vitamin D (2). Read below to learn more about vitamin D, the types of vitamin D supplements, and how much vitamin D you should be taking in each day.
Fast facts on vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is crucial in promoting calcium absorption in the gut as well as maintaining calcium and phosphate levels in the body (1). This in turn helps to ensure that the body has adequate nutrition to aid in bone growth and bone remodeling.
You can consume vitamin D in fatty fish like salmon, trout, or tuna as well as in fortified fruit juices and milk products. Sunlight exposure can also provide adequate vitamin D. between 5 to 30 minutes of daylight sun exposure at least twice weekly on the face, arm, hands, and legs without sunscreen can give you enough vitamin D to maintain optimal health.
How much vitamin D do you need each day?
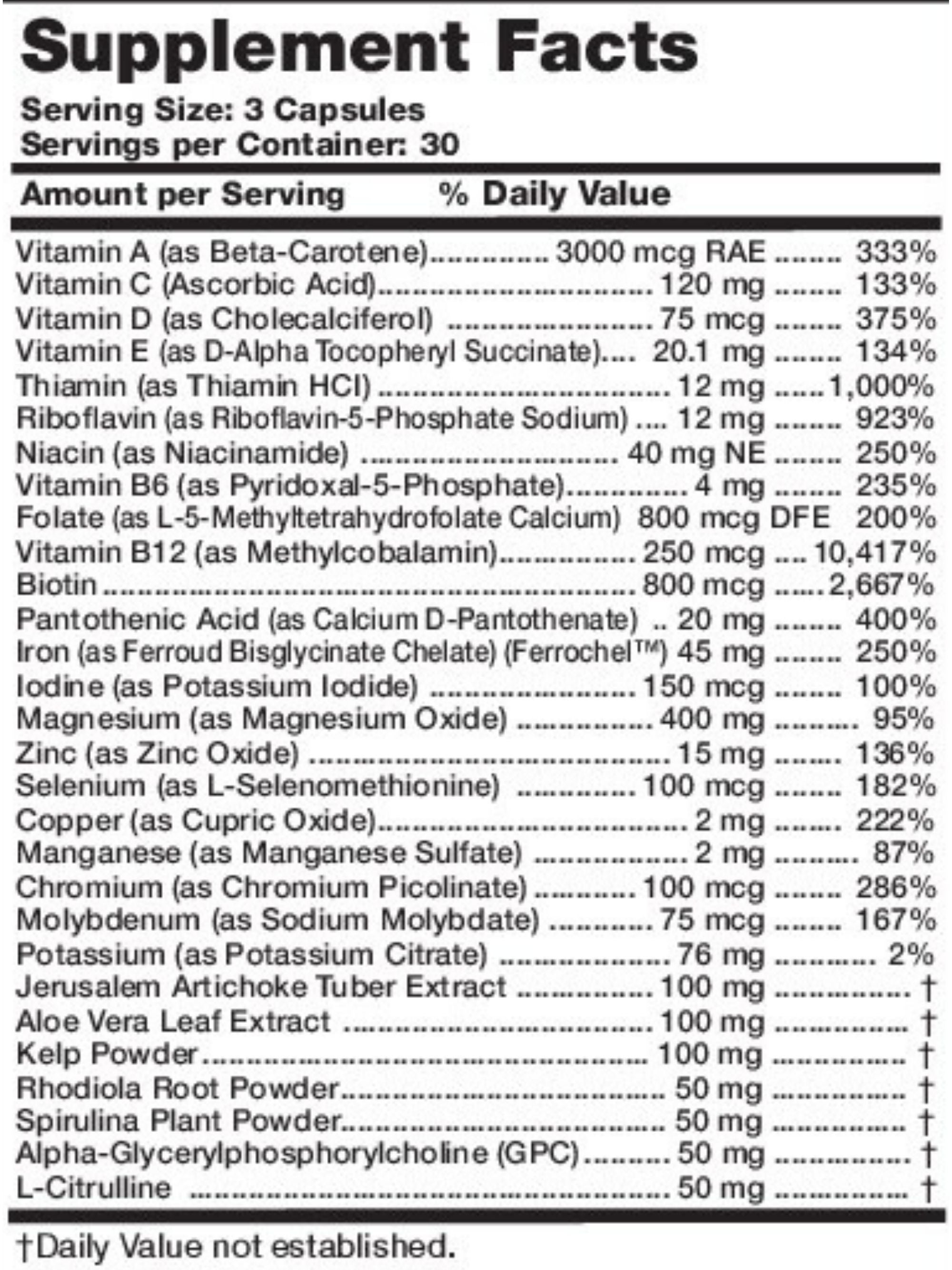
Most adults need at least 600 international units (IU) of vitamin D daily, with older adults over the age of 70 years needing about 800 IU daily (1,3). As of January 2021, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires manufacturers to use micrograms (mcg) per serving instead of International Units (IU) (1). About 40 IU is equal to 1 microgram of vitamin D, so the daily recommended dose of 600 IU for most adults would be equal to about 15 micrograms of vitamin D.
At-risk groups for vitamin D deficiency include older adults, those with fat malabsorption issues, as well as obese persons with a body mass index of 30 or greater (1). These individuals should be especially sure to have their vitamin D levels tested every year or so to make sure they are not vitamin D deficient.
Also, certain medicines may place you at risk for vitamin D deficiency such as laxatives, steroids like prednisone, certain cholesterol-lowering drugs, or certain weight loss drugs, for example (4).
Types of vitamin D supplements
There are two major types of vitamin D supplements known as high-dose prescription vitamin D2 and lower dose vitamin D3. Both types of vitamin D supplements are effective in raising vitamin D blood levels, but may be given for different reasons.
Vitamin D2 is made when the compound ergosterol from yeast is exposed to ultraviolet light, while D3 comes from fish or exposing lanolin from sheep’s wool to ultraviolet light (5). Both types of vitamin D have to pass through the liver and kidneys to convert itself to the active form of vitamin D used by the body.
Research shows that both forms of vitamin D are effective in improving vitamin D levels in the blood (6). The main difference between the two would be that D3 is animal-based, while D2 is plant-based (7).
Is vitamin D safe?
Taken in proper doses, vitamin D supplements are generally safe for most people to take. However, some people that take 4000 IU (100 micrograms) vitamin D may experience side effects like nausea, vomiting, constipation, and poor appetite, to name a few (4).
Bottom line on vitamin D
No matter what type of vitamin D you use, make sure your body is absorbing enough each day. You can check this by visiting your doctor at least every year to have your vitamin D levels checked. Then, if your levels are low, start on a supplement routine, soak up the sunlight more often, and supplement your diet with additional Vitamin D. Your bones and overall health will benefit because of it.
For additional learning on vitamin D
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
References:
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements (updated October 9, 2020) “Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.” https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
- Amrein, K., Scherkl, M., Hoffmann, M. et al. (2020). “Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide.” Eur J Clin Nutr, 74, 1498–1513.
- Mayo Clinic (October 18, 2017) “Vitamin D Overview.” https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-d/art-20363792
- Cleveland Clinic (last reviewed October 16, 2019) “Vitamin D Deficiency.” https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15050-vitamin-d--vitamin-d-deficiency
- Harvard Health Publishing Harvard Medical School (published February 2010) “On call: Vitamin D2 or D3?” https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/vitamin-d2-or-d3
- Shieh, A., et al. (2016). “Effects of High-Dose Vitamin D2 Versus D3 on Total and Free 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Markers of Calcium Balance.” The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 101(8), 3070–3078. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-1871








Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.